What are Zigbee Devices? 9 Things You Need to Know!
We’re reader-supported; we may earn a commission from links in this article.
Zigbee technology has been buzzing around the smart home industry, but what exactly is it, and how does it work?
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into Zigbee devices, exploring their benefits, applications, and how they can make your life more convenient.
From understanding the basics to setting up your own Zigbee network, we’ve got you covered.
Let’s get into it!
1. What is Zigbee?
Zigbee is a wireless communication protocol designed for low-power, short-range applications.
It’s often used in smart homes to connect various devices and create a seamless automation experience.
But how does this technology actually work?
2. How Does Zigbee Work?
Zigbee’s inner workings are a bit like a well-orchestrated dance among tiny devices. It’s fascinating to see how this wireless technology makes it all happen.
a. Zigbee Networking
Each Zigbee device in your smart home is like a guest at the party, and they’re all equipped with radios that can send and receive messages.
When one device wants to communicate with another, it doesn’t do so directly; instead, it passes the message to its closest neighbor. This neighbor, in turn, passes it along until it reaches the destination.
This relay system is what makes Zigbee so robust. If one device can’t reach the destination because of an obstacle or interference, another device steps in to help. It’s like a game of hot potato, but with data.
b. Mesh Topology
Now, let’s dive a bit deeper into this relay system. It’s called a mesh network, and it’s a bit like a spider’s web. Every Zigbee device is a node on this web, and they’re all connected to each other.
This redundancy is what gives Zigbee networks their strength. Even if a device fails or if there’s an obstruction, the network finds an alternative route for the data. It’s a bit like a road network where there’s always another path if one road is blocked.
3. Advantages of Zigbee Devices
Zigbee devices bring a lot to the table when it comes to creating a smart and connected home. Let’s explore some of the key advantages that make Zigbee a preferred choice for many homeowners.
a. Low Power Consumption
This low power consumption is a game-changer, especially for battery-operated devices like motion sensors and door/window sensors. You can expect these devices to last months, if not years, on a single set of batteries. This not only saves you money on replacements but also reduces the hassle of maintenance.
b. Interoperability
Zigbee devices follow standardized communication profiles. This means that Zigbee products from different manufacturers can talk to each other without any compatibility issues.
Whether you have a Zigbee light bulb from Brand A or a Zigbee smart plug from Brand B, they can work harmoniously within the same network.
This interoperability simplifies the setup process and gives you the freedom to choose the best devices for your needs, regardless of the brand.
c. Reliability
Thanks to its mesh network architecture, Zigbee is highly reliable. If one device can’t reach the hub due to distance or interference, another device will step in to relay the message.
This redundancy ensures that your smart home functions smoothly, even in challenging environments.
4. Top Zigbee Devices for Your Home
Zigbee is a popular wireless communication protocol used in smart home devices for its low power consumption, reliability, and compatibility with a wide range of products.
Here are some top Zigbee devices you can consider for your home:
a. Zigbee Hub (Coordinator)
A Zigbee hub serves as the central control unit for all your Zigbee devices. It connects to your home Wi-Fi network and allows you to manage and control all your Zigbee devices from a single app or interface.
Some of the best Zigbee hubs include the Samsung SmartThings Hub and the Philips Hue Bridge.
b. Zigbee Light Switch
Zigbee-enabled light switches can replace traditional ones and provide smart lighting control.
You can remotely dim or turn lights on and off using a smartphone app or voice commands via a smart assistant like Amazon Alexa or Google Assistant.
Products like the Lutron Aurora or the GE Zigbee Smart Switch are excellent choices.
c. Zigbee Thermostat
A Zigbee thermostat allows you to control your heating and cooling systems remotely. You can set schedules, monitor energy usage, and adjust the temperature using your smartphone or voice commands.
The Ecobee SmartThermostat with Zigbee support is a popular option.
d. Zigbee Repeater (Range Extender)
Zigbee repeaters enhance the range and reliability of your Zigbee network.
They help ensure signals can reach all corners of your home, especially for devices far from the hub. The IKEA TRÅDFRI Signal Repeater is a budget-friendly choice.
e. Zigbee Motion Sensor
Zigbee motion sensors are used for security and automation. They can trigger lights, cameras, or other devices when motion is detected.
The Samsung SmartThings Motion Sensor is a versatile Zigbee option.
f. Zigbee Button (Smart Remote)
Zigbee buttons or remotes can be placed anywhere in your home for quick control of smart devices. They can be programmed to perform various actions like turning off all lights or activating specific scenes.
The Philips Hue Smart Button is a compact and easy-to-use choice.
g. Zigbee Smart Plug
Zigbee smart plugs allow you to make non-smart devices, like lamps or small appliances, smart. They are great for energy monitoring and remote control. The Sengled Smart Plug or the Innr Smart Plug are reliable options.
h. Zigbee Bulb (Smart Light Bulb)
Zigbee smart bulbs can be controlled individually or as part of lighting scenes. They often offer features like color-changing options and scheduling.
The Philips Hue Bulbs are among the most popular Zigbee lighting solutions.
i. Zigbee Door Lock
Zigbee door locks provide keyless entry and remote access control for your home.
You can lock or unlock your door from your smartphone and receive notifications when someone enters or exits. The Yale Assure Lock with Zigbee is a secure and widely compatible option.
5. Setting Up Your Zigbee Network
Now that you’re intrigued by the possibilities of Zigbee devices, it’s time to set up your own Zigbee network. This section will guide you through the process, from choosing the right Zigbee hub to ensuring the security of your network.
a. Choosing a Zigbee Hub
A Zigbee hub, also known as a Zigbee gateway or coordinator, is the central brain of your Zigbee network.
The device communicates with all your Zigbee-enabled gadgets and ensures they work together seamlessly.
When selecting a Zigbee hub, consider compatibility with the devices you plan to use. Some hubs are designed to work best with specific brands or ecosystems, so make sure your hub supports the devices you want to connect.
Popular choices for Zigbee hubs include brands like SmartThings, Hubitat, and Philips Hue Bridge. These hubs often provide user-friendly apps for easy device management.
b. Pairing Zigbee Devices
Once you have your Zigbee hub in hand, it’s time to pair your Zigbee devices with it.
This process may vary slightly depending on your hub and devices, but the general steps are as follows:
- Put your Zigbee hub in pairing mode: Usually, this involves opening your hub’s app and following the instructions to put it in pairing or discovery mode.
- Prepare your Zigbee device: Check the manufacturer’s instructions for your device. Typically, this involves putting the device in pairing mode (e.g., pressing a button or holding it for a few seconds).
- Wait for the connection: Your hub and device should automatically detect each other. Once they do, you’ll see the new device pop up in your hub’s app.
- Name your device: Give your device a recognizable name to make it easier to control. For instance, “Living Room Light” or “Front Door Sensor.”
- Test and configure: Test your newly paired device to ensure it works as expected. Depending on the device, you may also have options to customize its behavior in the hub’s app.
c. Network Security
Ensuring the security of your Zigbee network is crucial to protect your privacy and prevent unauthorized access. Here are some essential security measures:
- Change default passwords: If your Zigbee hub or devices come with default login credentials, change them immediately to something strong and unique.
- Enable network encryption: Most Zigbee hubs offer encryption options. Enable this feature to protect data transmitted between your devices.
- Keep firmware updated: Regularly update your hub’s firmware and the firmware of connected Zigbee devices. Manufacturers often release updates that patch security vulnerabilities.
- Use strong Wi-Fi security: Since your Zigbee hub likely connects to your home Wi-Fi network, ensure your Wi-Fi is secure with a strong password.
- Isolate guest networks: If your Wi-Fi router supports guest networks, consider placing your IoT devices on a separate, isolated network to prevent them from accessing your main network.
- Regularly review connected devices: Periodically review the devices connected to your Zigbee network. If you no longer use a device, remove it to reduce potential security risks.
6. Common Applications of Zigbee
Zigbee technology is versatile and finds application in various aspects of modern life. Here are some common and practical uses of Zigbee devices:
a. Smart Lighting
Zigbee-enabled light bulbs have revolutionized home lighting. They allow you to control the brightness and color of your lights remotely using your smartphone or voice commands. Create lighting scenes for different occasions or schedules to simulate your presence when you’re away.
b. Home Security Systems
Zigbee plays a crucial role in enhancing home security.
Devices like door/window sensors, motion detectors, and smart locks can connect through Zigbee.
If an intruder tries to enter your home, you’ll receive instant notifications on your smartphone, giving you peace of mind and control over your home’s security.
c. Smart Thermostats
Imagine being able to adjust your home’s temperature from anywhere, ensuring comfort and energy efficiency.
Zigbee-enabled thermostats make this possible. They integrate seamlessly with other smart devices, like smart blinds and HVAC systems, to create an energy-efficient and comfortable living environment.
d. Home Automation
Zigbee is at the core of home automation. From controlling your coffee maker to managing your home theater system, Zigbee devices can automate various tasks. Set routines and schedules to streamline your daily life and save time.
e. Asset Tracking
Zigbee’s low-power capabilities make it suitable for asset tracking in various industries.
In warehouses or healthcare settings, Zigbee can be used to track the location of valuable equipment, ensuring efficient operations and reducing loss.
f. Healthcare Monitoring
In the healthcare sector, Zigbee is used for patient monitoring. Wearable devices equipped with Zigbee technology can transmit vital signs and other health data to healthcare providers in real time, enabling better patient care and early intervention.
g. Industrial Automation
Zigbee extends beyond homes and into the industrial realm.
t’s employed in industrial automation to monitor machinery, control processes, and improve overall efficiency. Zigbee’s reliability and low power consumption make it a valuable choice for this application.
h. Agriculture
Even agriculture benefits from Zigbee technology.
Zigbee-based sensors can monitor soil conditions, weather, and crop health, helping farmers make informed decisions and optimize crop yield.
i. Lighting Control in Commercial Buildings
Zigbee is used for lighting control in larger-scale applications, such as commercial buildings.
Building managers can adjust lighting levels to save energy and create comfortable work environments, all while ensuring seamless communication between devices.
j. Smart Energy Management
Zigbee is instrumental in smart energy management solutions. From monitoring and controlling energy consumption in homes to managing grid efficiency at a larger scale, Zigbee helps reduce energy waste and lower costs.
7. Troubleshooting Common Zigbee Issues
While Zigbee networks are known for their reliability, occasional hiccups can occur. Here are some common Zigbee issues and how to troubleshoot them:
a. Signal Interference
Problem: Zigbee operates on the 2.4 GHz band, which can be crowded with other wireless devices like Wi-Fi routers, microwaves, and cordless phones. Interference can disrupt your Zigbee network.
Solution:
- Change Zigbee channel: Most Zigbee hubs allow you to change the operating channel. Experiment with different channels to find one with less interference.
- Reposition devices: Move Zigbee devices closer to the hub to improve signal strength and reduce interference.
- Upgrade your Wi-Fi router: If your Wi-Fi and Zigbee networks overlap, consider upgrading to a dual-band router that can segregate traffic on the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands.
b. Device Connectivity Problems
Problem: Occasionally, Zigbee devices may disconnect or fail to respond.
Solution:
- Check power sources: Ensure that battery-powered devices have adequate power or that wired devices are correctly connected.
- Re-pair devices: Re-pairing a device with the Zigbee hub can sometimes resolve connectivity issues. Follow the pairing instructions for your specific device.
- Hub placement: Ensure your Zigbee hub is centrally located to provide the best coverage to all devices.
- Check for interference: Verify that there are no new sources of interference near your Zigbee devices.
- Firmware updates: Check for firmware updates for your Zigbee hub and devices. Manufacturers often release updates to improve compatibility and reliability.
c. Slow Response Times
Problem: You notice delays when controlling Zigbee devices.
Solution:
- Network congestion: Excessive traffic on your Zigbee network can cause delays. Limit the number of devices actively communicating at once.
- Router and hub restart: Reboot your router and Zigbee hub occasionally to refresh network connections.
- Optimize automation routines: If you have complex automation routines, streamline them to reduce the number of commands sent simultaneously.
- Reduce device load: If possible, reduce the number of devices connected to a single Zigbee network to reduce overall traffic.
d. Range Issues
Problem: Zigbee devices may not reach all areas of your home or property.
Solution:
- Add more devices: Expanding your network with additional Zigbee devices can extend its range.
- Use Zigbee repeaters: Invest in Zigbee repeater devices to extend the network coverage. These devices amplify the signal and can help reach distant areas.
- Optimize placement: Ensure that your Zigbee devices are strategically placed to create a robust mesh network, covering dead spots.
- Check for obstacles: Large metal objects, concrete walls, or other obstacles can block signals. Reposition devices to minimize obstructions.
e. Device Compatibility
Problem: Certain Zigbee devices may not work well with others due to compatibility issues.
Solution:
- Check compatibility: Verify their compatibility with your Zigbee hub before adding new devices to your Zigbee network. Manufacturers often provide lists of compatible devices.
- Update firmware: Ensure all your Zigbee devices are running the latest versions to enhance compatibility.
- Grouping devices: If you experience issues with specific device combinations, consider grouping them and controlling them as a single entity within your automation routines.
8. The Future of Zigbee
As technology evolves and the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand, Zigbee remains poised to play a significant role in shaping the future of connected devices and smart homes.
Let’s explore some key developments and the potential trajectory of Zigbee technology:
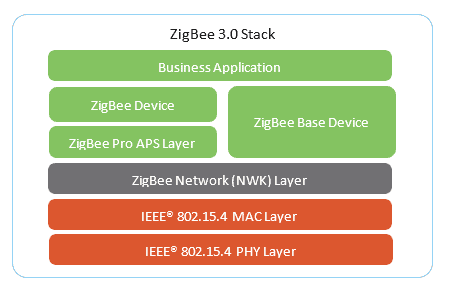
a. Zigbee 3.0 Standard
Zigbee 3.0 represents the latest standardization effort in Zigbee technology. This standard unifies various Zigbee profiles into a single, comprehensive standard.
It simplifies device compatibility, making it easier for consumers to build interconnected smart home ecosystems with devices from different manufacturers.
Zigbee 3.0 also enhances security, enabling secure communication between devices, and improves energy efficiency, extending the battery life of Zigbee devices.
b. IoT Integration
The Internet of Things (IoT) is all about connecting everyday objects to the internet, enabling them to collect and exchange data.
Zigbee is well-positioned to be a fundamental technology in the IoT landscape due to its low-power, low-data-rate capabilities and ability to create large-scale mesh networks.
9. Zigbee and Privacy
Privacy is a critical concern in the world of IoT and smart home technology, and Zigbee has implemented measures to address these concerns. Here’s how Zigbee helps protect your privacy:
a. Encryption and Security
Zigbee employs robust security measures to ensure that your data remains private and secure:
- AES Encryption: Data transmitted between Zigbee devices is typically encrypted using Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) encryption. This encryption makes it extremely difficult for unauthorized parties to intercept and decipher the data.
- Authentication: Zigbee devices often use authentication mechanisms to verify the identity of devices on the network. This prevents unauthorized devices from gaining access to your Zigbee network.
b. Local Processing
Many Zigbee devices are designed for local processing, which means that sensitive data is processed directly on the device itself or within your home, rather than being sent to a cloud server.
This local processing reduces the risk of your personal data being stored or accessed by third parties.
c. User Control
Zigbee networks are designed to give users control over their devices and data:
- Device Permissions: Users can set permissions and access levels for each device on their Zigbee network. This allows you to control who can interact with your devices and access your data.
- Data Access: Zigbee hubs and controllers typically provide tools for users to monitor and control the data their devices generate. You can review and delete data as needed, enhancing your control over your information.
d. Data Minimization
Zigbee devices are often designed to collect only the data necessary for their intended purpose. This data minimization approach reduces the amount of potentially sensitive information generated by your devices.
e. Manufacturer Privacy Policies
When using Zigbee devices, it’s essential to review the privacy policies of the manufacturers and the hubs or controllers you use.
These policies outline how your data is collected, stored, and used. Choose manufacturers and platforms that align with your privacy preferences.
f. Regular Updates
Manufacturers of Zigbee devices often release firmware updates that include security enhancements.
Keeping your devices and hub firmware up-to-date is crucial for maintaining a secure and private Zigbee network.
c. User Awareness
To maintain privacy in your Zigbee network, it’s essential to stay informed about potential security risks and best practices.
Regularly review your network settings, user permissions, and connected devices to maintain your privacy.
Conclusion
Zigbee technology has emerged as a powerful force in the world of smart homes and the Internet of Things (IoT).
It offers numerous advantages, including low power consumption, interoperability, and reliability, making it a top choice for creating interconnected ecosystems of smart devices.
FAQs About Zigbee Devices
Q1. Are Zigbee devices compatible with voice assistants like Alexa and Google Assistant?
Yes, many Zigbee devices can be integrated with popular voice assistants, allowing you to control them using voice commands.
Q2. Can I mix and match Zigbee devices from different manufacturers?
Yes, Zigbee’s interoperability standards ensure that devices from different manufacturers can work together seamlessly.
Q3. Is Zigbee secure against hacking and cyber threats?
Zigbee networks can be secured with encryption and authentication measures, but it’s essential to follow best practices to protect your smart home.
Q4. How far can Zigbee devices communicate within a network?
The range of Zigbee devices can vary, but they typically have a range of up to 100 meters (328 feet) in open spaces.
Q5. What’s the difference between Zigbee and Wi-Fi for smart home applications?
Zigbee is designed for low-power, short-range applications, while Wi-Fi offers higher data transfer speeds and is better suited for devices that require a continuous internet connection. Choose the technology that best fits your specific needs.

Justin Chia
Justin is the author of Justjooz and is a data analyst and AI expert. He is also a Nanyang Technological University (NTU) alumni, majoring in Biological Sciences.
He regularly posts AI and analytics content on LinkedIn, and writes a weekly newsletter, The Juicer, on AI, analytics, tech, and personal development.
To unwind, Justin enjoys gaming and reading.